漏洞分析
IOST公链使用Go语言开发,Go语言的make函数如果参数控制不当容易产生拒绝服务漏洞。在IOST的公链代码中搜索make,找到了一处貌似可以利用的地方。
func (sy *SyncImpl) getBlockHashes(start int64, end int64) *msgpb.BlockHashResponse {
resp := &msgpb.BlockHashResponse{
BlockInfos: make([]*msgpb.BlockInfo, 0, end-start+1),
}
node := sy.blockCache.Head()
if node != nil && end > node.Head.Number {
end = node.Head.Number
}
省略...
Line3 make的第3个参数为end-start+1, end和start来自handleHashQuery
func (sy *SyncImpl) handleHashQuery(rh *msgpb.BlockHashQuery, peerID p2p.PeerID) {
if rh.End < rh.Start || rh.Start < 0 {
return
}
var resp *msgpb.BlockHashResponse
switch rh.ReqType {
case msgpb.RequireType_GETBLOCKHASHES:
resp = sy.getBlockHashes(rh.Start, rh.End)
case msgpb.RequireType_GETBLOCKHASHESBYNUMBER:
resp = sy.getBlockHashesByNums(rh.Nums)
}
省略...
可以看到并没有限制end-start+1的大小,只要end足够大,start足够小就可以导致拒绝服务。所以现在问题就只剩下如何触发这个漏洞。
漏洞利用
IOST节点之间的P2P通信使用的是libp2p,libp2p是一个模块化的网络堆栈,汇集了各种传输和点对点协议,使开发人员可以轻松构建大型,强大的p2p网络。
来看一看IOST节点的P2P service启动流程。
首先创建一个NetService,代码如下:
// NewNetService returns a NetService instance with the config argument.
func NewNetService(config *common.P2PConfig) (*NetService, error) {
ns := &NetService{
config: config,
}
if err := os.MkdirAll(config.DataPath, 0755); config.DataPath != "" && err != nil {
ilog.Errorf("failed to create p2p datapath, err=%v, path=%v", err, config.DataPath)
return nil, err
}
privKey, err := getOrCreateKey(filepath.Join(config.DataPath, privKeyFile))
if err != nil {
ilog.Errorf("failed to get private key. err=%v, path=%v", err, config.DataPath)
return nil, err
}
host, err := ns.startHost(privKey, config.ListenAddr)
if err != nil {
ilog.Errorf("failed to start a host. err=%v, listenAddr=%v", err, config.ListenAddr)
return nil, err
}
ns.host = host
ns.PeerManager = NewPeerManager(host, config)
ns.adminServer = newAdminServer(config.AdminPort, ns.PeerManager)
return ns, nil
}
主要看Line18的startHost,该函数调用libp2p库创建了一个host
// startHost starts a libp2p host.
func (ns *NetService) startHost(pk crypto.PrivKey, listenAddr string) (host.Host, error) {
tcpAddr, err := net.ResolveTCPAddr("tcp", listenAddr)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if !isPortAvailable(tcpAddr.Port) {
return nil, ErrPortUnavailable
}
opts := []libp2p.Option{
libp2p.Identity(pk),
libp2p.NATPortMap(),
libp2p.ListenAddrStrings(fmt.Sprintf("/ip4/%s/tcp/%d", tcpAddr.IP, tcpAddr.Port)),
libp2p.Muxer(protocolID, mplex.DefaultTransport),
}
h, err := libp2p.New(context.Background(), opts...)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
h.SetStreamHandler(protocolID, ns.streamHandler)
return h, nil
}
该host的流处理逻辑在ns.streamHandler中
func (ns *NetService) streamHandler(s libnet.Stream) {
ns.PeerManager.HandleStream(s, inbound)
}
steamHandler又调用PeerManager的HandleStream函数
// HandleStream handles the incoming stream.
//
// It checks whether the remote peer already exists.
// If the peer is new and the neighbor count doesn't reach the threshold, it adds the peer into the neighbor list.
// If peer already exits, just add the stream to the peer.
// In other cases, reset the stream.
func (pm *PeerManager) HandleStream(s libnet.Stream, direction connDirection) {
remotePID := s.Conn().RemotePeer()
pm.freshPeer(remotePID)
if pm.isStreamBlack(s) {
ilog.Infof("remote peer is in black list. pid=%v, addr=%v", remotePID.Pretty(), s.Conn().RemoteMultiaddr())
s.Conn().Close()
return
}
ilog.Debugf("handle new stream. pid=%s, addr=%v, direction=%v", remotePID.Pretty(), s.Conn().RemoteMultiaddr(), direction)
peer := pm.GetNeighbor(remotePID)
if peer != nil {
s.Reset()
return
}
if pm.NeighborCount(direction) >= pm.neighborCap[direction] {
if !pm.isBP(remotePID) {
ilog.Infof("neighbor count exceeds, close connection. remoteID=%v, addr=%v", remotePID.Pretty(), s.Conn().RemoteMultiaddr())
if direction == inbound {
bytes, _ := pm.getRoutingResponse([]string{remotePID.Pretty()})
if len(bytes) > 0 {
msg := newP2PMessage(pm.config.ChainID, RoutingTableResponse, pm.config.Version, defaultReservedFlag, bytes)
s.Write(msg.content())
}
time.AfterFunc(time.Second, func() { s.Conn().Close() })
} else {
s.Conn().Close()
}
return
}
pm.kickNormalNeighbors(direction)
}
pm.AddNeighbor(NewPeer(s, pm, direction))
return
}
对于新建立连接的peer,IOST会启动该peer并添加到neighbor list中
// AddNeighbor starts a peer and adds it to the neighbor list.
func (pm *PeerManager) AddNeighbor(p *Peer) {
pm.neighborMutex.Lock()
defer pm.neighborMutex.Unlock()
if pm.neighbors[p.id] == nil {
p.Start()
pm.storePeerInfo(p.id, []multiaddr.Multiaddr{p.addr})
pm.neighbors[p.id] = p
pm.neighborCount[p.direction]++
}
}
peer启动之后,IOST会调用peer的readLoop和writeLoop函数对该peer进行读写。
// Start starts peer's loop.
func (p *Peer) Start() {
ilog.Infof("peer is started. id=%s", p.ID())
go p.readLoop()
go p.writeLoop()
}
我们主要看readLoop,看IOST对我们发送的数据如何处理。
func (p *Peer) readLoop() {
header := make([]byte, dataBegin)
for {
_, err := io.ReadFull(p.stream, header)
if err != nil {
ilog.Warnf("read header failed. err=%v", err)
break
}
chainID := binary.BigEndian.Uint32(header[chainIDBegin:chainIDEnd])
if chainID != p.peerManager.config.ChainID {
ilog.Warnf("mismatched chainID. chainID=%d", chainID)
break
}
length := binary.BigEndian.Uint32(header[dataLengthBegin:dataLengthEnd])
if length > maxDataLength {
ilog.Warnf("data length too large: %d", length)
break
}
data := make([]byte, dataBegin+length)
_, err = io.ReadFull(p.stream, data[dataBegin:])
if err != nil {
ilog.Warnf("read message failed. err=%v", err)
break
}
copy(data[0:dataBegin], header)
msg, err := parseP2PMessage(data)
if err != nil {
ilog.Errorf("parse p2pmessage failed. err=%v", err)
break
}
tagkv := map[string]string{"mtype": msg.messageType().String()}
byteInCounter.Add(float64(len(msg.content())), tagkv)
packetInCounter.Add(1, tagkv)
p.handleMessage(msg)
}
p.peerManager.RemoveNeighbor(p.id)
}
主要是读取一个固定长度的header,然后根据header中的length来读取data,通过header和data创建一个P2PMessage,最后调用handleMessage来处理这个msg。
节点发送的数据包结构如下:
/*
P2PMessage protocol:
0 1 2 3 (bytes)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| Chain ID |
+-------------------------------+-------------------------------+
| Message Type | Version |
+-------------------------------+-------------------------------+
| Data Length |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| Data Checksum |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| Reserved |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
. Data .
| |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
*/
handleMessage会根据messageType对message进行处理
// HandleMessage handles messages according to its type.
func (pm *PeerManager) HandleMessage(msg *p2pMessage, peerID peer.ID) {
data, err := msg.data()
if err != nil {
ilog.Errorf("get message data failed. err=%v", err)
return
}
switch msg.messageType() {
case RoutingTableQuery:
go pm.handleRoutingTableQuery(msg, peerID)
case RoutingTableResponse:
go pm.handleRoutingTableResponse(msg)
default:
inMsg := NewIncomingMessage(peerID, data, msg.messageType())
if m, exist := pm.subs.Load(msg.messageType()); exist {
m.(*sync.Map).Range(func(k, v interface{}) bool {
select {
case v.(chan IncomingMessage) <- *inMsg:
default:
ilog.Warnf("sending incoming message failed. type=%s", msg.messageType())
}
return true
})
}
}
}
了解了IOST节点之间P2P通信的处理逻辑,再来看看如何触发存在漏洞的handleHashQuery函数。
messageLoop中调用了handlerHashQuery
func (sy *SyncImpl) messageLoop() {
defer sy.wg.Done()
for {
select {
case req := <-sy.messageChan:
switch req.Type() {
case p2p.SyncBlockHashRequest:
var rh msgpb.BlockHashQuery
err := proto.Unmarshal(req.Data(), &rh)
if err != nil {
ilog.Errorf("Unmarshal BlockHashQuery failed:%v", err)
break
}
go sy.handleHashQuery(&rh, req.From())
省略...
可以看到当messageType为p2p.SyncBlockHashRequest,Data为BlockHashQuery时,handlerHashQuery函数会被调用。
BlockHashQuery的结构如下, End和Start的值可控。
type BlockHashQuery struct {
ReqType RequireType `protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=reqType,proto3,enum=msgpb.RequireType" json:"reqType,omitempty"`
Start int64 `protobuf:"varint,2,opt,name=start,proto3" json:"start,omitempty"`
End int64 `protobuf:"varint,3,opt,name=end,proto3" json:"end,omitempty"`
Nums []int64 `protobuf:"varint,4,rep,packed,name=nums,proto3" json:"nums,omitempty"`
XXX_NoUnkeyedLiteral struct{} `json:"-"`
XXX_unrecognized []byte `json:"-"`
XXX_sizecache int32 `json:"-"`
}
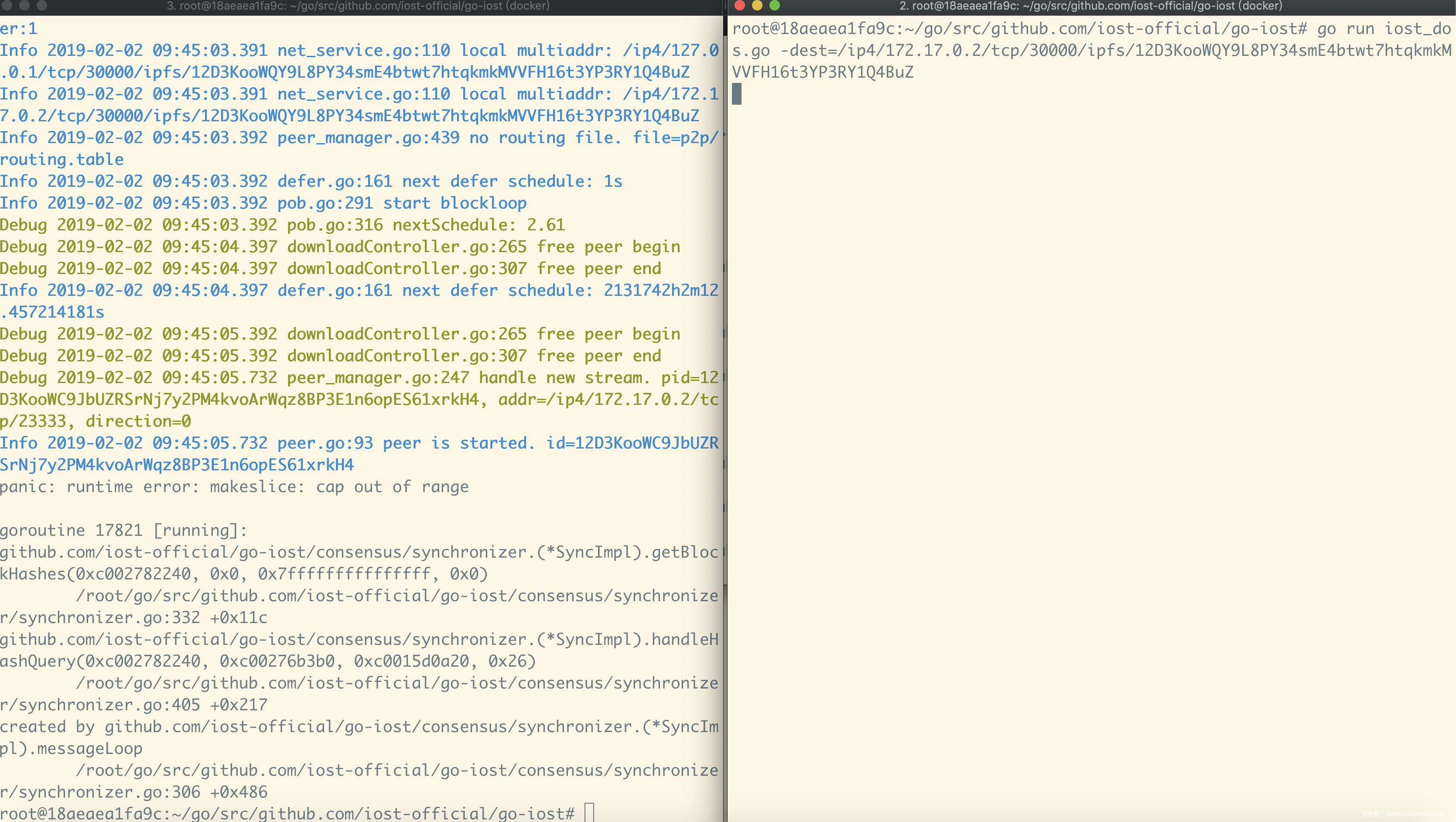
因此,我们可以构造一个Message,将Start的值设为0,End的值设为math.MaxInt64,将该Message发送给节点,就可以触发make函数的cap out of range,导致拒绝服务。
POC见 https://github.com/fatal0/poc/blob/master/go-iost/p2p_dos.go
漏洞修复
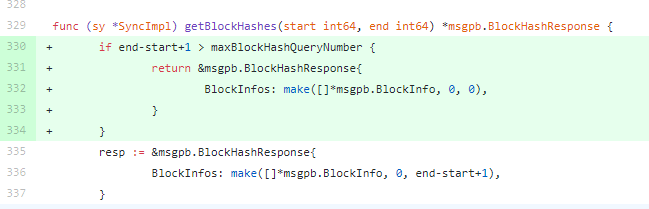
官方的修复方式也很简单,限制end-start+1的大小。








发表评论
您还未登录,请先登录。
登录